- Visibility 189 Views
- Downloads 30 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijpo.2020.080
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Expression of p16 in cervical premalignant and malignant lesions- IHC study
- Author Details:
-
Bharadwaj Vedula *
-
Rama Reddy B V
-
Rajani M
-
Sree Ramulu Naidu R
-
Srikanth Reddy K
Introduction
Cancer of the cervix uteri is the 4th most common cancer among women worldwide[1] and ranks as the 2nd leading cause of female cancer in India.[2] HPV causes the majority of cervical cancer cases. Human genomic integration of the high-risk HPV viral genome causes up-regulation of the tumor suppressor gene P16INK4A. The protein p16 is integral to pRb (Retinoblastoma) mediated G1-S phase transition of the cell cycle which acts by inactivating the CDKs that phosphorylate Rb protein. Reciprocal relation between p16 and pRb was noticed. The E7 protein of the Human papillomavirus binds and inactivates Rb which leads to the release of E2F, a transcription factor, which in turn can turn on the genes required for entry into the S phase of the cell cycle. This augments the levels of p16 through a negative feedback mechanism. Accumulation of E2F has also been found to increase P16 transcription.[3], [4]
The protein p16INK4a serves as a surrogate marker for the oncogenic activities of HPV in replication-competent cells of cervical epithelium, and its overexpression is well established in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and invasive cancer by many studies.[5], [6] A potential biomarker should distinguish between cervical intraepithelial Neoplasms (CIN) and other non-neoplastic cervical lesions. HPV detection can be done using p16INK4a as a diagnostic marker by immunohistochemical staining method to show the varied intensity and expression in increasing grades of uterine cervical dysplasia and malignancy.[7]
Materials and Methods
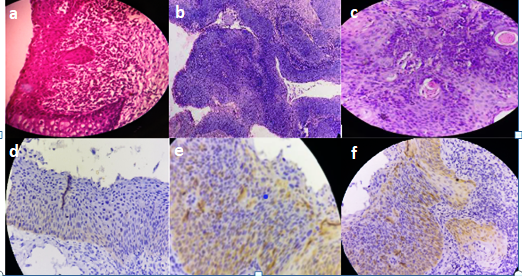
In this prospective study from July 2016 to June 2018, total number of 86 cases of uterine cervical premalignant lesions and malignant neoplasms diagnosed in the Department of Pathology, Siddhartha medical college, Vijayawada were included. All the specimens obtained were fixed in 10% buffered formalin and were submitted in Toto for routine tissue processing. Paraffin-embedded tissues were sectioned and stained with Haematoxylin and eosin. All 86 Cases were selected for IHC to detect the intensity of HPV. For Immunohistochemistry, paraffin-embedded tissue sections were floated on chromalum coated slides. The antigen retrieval was done by using Tris buffer. The sections were stained using a standard peroxidase- antiperoxidase technique. The slides were incubated with primary monoclonal antibody- p16 (a mouse monoclonal anti-p-16 antibody, Fremont, CA, Biogenex, USA) for one and a half hours. The chromogen used was DiaminoBenzidine (DAB), after incubation with secondary polymer antibody for 30 minutes, counterstaining was done with Haematoxylin and coverslipped. The p16 immunostaining was considered positive when the nucleus and or cytoplasm took brown colour in at least 1% of tumor cells. Different methods had been used for scoring p16 immunostaining in several studies. However, the following parameters were considered in the scoring of p16 positive cells in the present study. Scoring was semi-quantitative based on the following. The intensity of staining was graded between 0-3. (Table 3). Negative –Grade 0, Weak focally positive – Grade 1+, Moderate -- (Weak, diffusely positive or strong focally positive) – Grade 2+, Strong -- (strong diffusely positive) – Grade 3+. Grade 0 was considered negative for p16INK4a staining, while Grade 1 to Grade 3 were considered positive for p16INK4a. p-value was calculated for various premalignant lesions, and invasive carcinoma versus p16 expression using the chi-square test and p-value obtained was <0.05 which is statistically significant.
Results
The study included 86 cases of cervical dysplastic and malignant lesions. The most common lesion was Squamous cell carcinoma (35 cases, 40.60%), followed by HSIL (24 cases, 27.9%), LSIL (20 cases, 23.25%), adenocarcinoma (6 cases, 6.97%), and adenosquamous carcinoma (1 case, 1.16%) ([Table 1]).
| Lesion | Number of cases |
| LSIL | 20(23.25%) |
| HSIL | 24(27.9%) |
| Carcinoma | 42(48.83%) |
| Total | 86 |
| Types | LSIL | HSIL | Carcinoma |
| Positive | 8 (40%) | 17 (70.83%) | 37 (88.09%) |
| Negative | 12 (60%) | 7(29.16%) | 5 (11.9%) |
| Total | 20 | 24 | 42 |
| Category | The intensity of p16INK4a staining | |||
| 0 (Negative) | 1+ (Weak) | 2+ (Moderate) | 3+ (Strong) | |
| LSIL | 12(60%) | 6(30%) | 2(10%) | 0 |
| HSIL | 7(29.16%) | 5(20.83%) | 8(33.33%) | 4(16.66%) |
| SCC | 4(11.42%) | 0 | 10(28.57%) | 21(60%) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 1(16.66%) | 0 | 1(16.66%) | 4(66.66%) |
| Adenosquamous carcinoma | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1(100%) |
| Total | 24 | 13 | 22 | 27 |
Discussion
In the present study, there were 20 cases of LSIL, 24 cases of HSIL and 42 cases of invasive cervical carcinoma in histopathology. Among them, p16INK4a was found to be positive in 8 cases of LSIL, 17 cases of HSIL and 37 cases of cervical Carcinoma (Table 2). The percentage of overall p16 positivity in this study was 72.09% which was close to that of Chaloob et al. (74.28%) and Supriya et al. (76.1%). Many studies have emphasized the significance of using p16INK4a immunostain as a marker for identifying dysplastic and neoplastic lesions caused by high-risk HPV.[8] The staining intensity of p16INK4A varies with the amount of dysplasia. As the grade of dysplasia increases, there is an increased expression of p16INK4A.[9], [10] In this study, most of the LSIL cases were p16INK4a negative (60%). The high percentage of negativity of p16INK4a in LSIL may be due to latent or subclinical HPV infection with a low viral load that may be insufficient for p16INK4a expression. The other possible reason for the lower expression of p16INK4a in LSIL may be because a certain percentage is thought to be caused by low-risk HPV types.[11] Previous studies indicated that viral oncoprotein of low-risk HPV such as HPV-6 does not affect p16INK4a because the affinity of HPV-6 E7 protein for cellular pRb is ten-fold lower than that of HPV-16 E7 for pRb.[12]
In this study, 70.83% of HSIL and 88.09% of cervical carcinomas show p16INK4a over-expression, which emphasizes the important causal relationship between HPV and cervical cancer. However, a few patients with HSIL and cervical cancer had p16INK4a negativity respectively. The possible explanation for the absence of p16INK4a expression in these high-grade lesions could be methylation of the p16INK4a promoter resulting in silencing of the p16 INK4A gene.[13] These findings were similar to those of study by Umar et al (HSIL-81.81%, Carcinoma- 88.52%) which also found that p16 INK4A expression was directly related to the increasing grade of CIN.[9]
p16 is primarily a nuclear protein, and hence immunohistochemical expression should show nuclear staining. However, in dysplasia, both nuclear and cytoplasmic staining is observed possibly because of post-transcriptional modification or overproduction of p16 protein forcing its transfer into the cytoplasm.[14] Among p16-positive cases, this study identified a direct relationship between lesion severity and reaction intensity. The frequency of positive cells and the reaction intensity were statistically significantly different when compared among different histological groups. The immunoreactivity for p16 in squamous cell carcinoma is unequivocally shown by all studies to date and has been confirmed by this study as well ([Table 4]).
| Author | Year | Normal | CIN I(LSIL) | HSIL | Carcinoma | |
| CIN II | CIN III | |||||
| Kumari K | 2013 | 25% (4/16) | 62.5% (10/16) | 75% (12/16) | 81.2% (13/16) | 100% (16/16) |
| Umar et al | 2016 | 0% (0/5) | 0% (0/6) | 80% (4/5) | 83.33% (5/6) | 88.52% (54/61) |
| Chaloob et al | 2016 | 0% (0/22) | 37.5% (9/24) | 67.9% (19/28) | 94.3% (50/53) | |
| Vatsala Kishore | 2017 | 0% (0/20) | 25% (1/4) | 50% (1/2) | 75% (3/4) | 100% (47/47) |
| Present study | 2018 | Not included | 40% (8/20) | 70.83% (17/24) | 88.09% (37/42) |
Conclusion
The neoplastic transformation of cervical epithelial cells by HPV can be detected byp16INK4a expression. Overexpression of the protein p16INK4a is a characteristic feature of dysplastic and neoplastic cervical epithelial cells. The expression of P16INK4a positivity increases with increasing grades of dysplasia (Carcinoma>HSIL>LSIL). P16 negative high-grade lesions also exist as reported by Valgareva et al (2004). Henceforth, our study reiterated that the protein p16INK4a can be used as a specific diagnostic marker of cervical dysplastic and neoplastic lesions.
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Freddie Bray, Jacques Ferlay, Isabelle Soerjomataram, Rebecca L. Siegel, Lindsey A. Torre, Ahmedin Jemal. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA: A Cancer J Clin 2018. [Google Scholar]
- L Bruni, L Barrionuevo-Rosas, G Albero, M Aldea, B Serrano, S Valencia. Institute Català d’Oncologia) Information Centre on HPV and Cancer (HPV Information Centre). Human Papillomavirus and Related Diseases. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kalpana Kumari. Akhila Arcot Vadivelan.P16INK4A expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer. Brunei Int Med J 2013. [Google Scholar]
- P Sasieni, A Castanon, J Cuzick. Effectiveness of cervical screening with age: Population-based case-control study of prospectively recorded data. BMJ 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ruediger Klaes, Tibor Friedrich, Dimitry Spitkovsky, Ruediger Ridder, Wolfgang Rudy, Ulrich Petry. Overexpression of p16INK4A as a specific marker for dysplastic and neoplastic epithelial cells of the cervix uteri. Int J Cancer 2001. [Google Scholar]
- J Doorbar. Molecular biology of human papillomavirus infection and cervical cancer. Clin Sci (Lond) 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Geok Chin Tan. Immunostaining study in P16INK4A and surviving cervical squamous neoplasm. Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Takaaki Sano, Tetsunari Oyama, Kenji Kashiwabara, Toshio Fukuda, Takashi Nakajima. Expression Status of p16 Protein Is Associated with Human Papillomavirus Oncogenic Potential in Cervical and Genital Lesions. Am J Pathol 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Umar. Immunohistochemical expression of p16INK4A protein in cervical dysplasia and carcinoma in patients attending federal teaching hospital. Afr J Cell Pathol 2016. [Google Scholar]
- K G Padmanaban, A L Santhl. Evaluation of P16INK4a status as a biomarker for uterine cervical neoplasms. J Curr Trends Clin Med Lab Biochem 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Giovanni Negri, Fabio Vittadello, Fabio Romano, Armin Kasal, Francesco Rivasi, Salvatore Girlando. p16INK4a expression and progression risk of low-grade intraepithelial neoplasia of the cervix uteri. Virchows Arch 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Christine Bergeron, Guglielmo Ronco, Miriam Reuschenbach, Nicolas Wentzensen, Marc Arbyn, Mark Stoler. The clinical impact of using p16INK4aimmunochemistry in cervical histopathology and cytology: An update of recent developments. Int J Cancer 2015. [Google Scholar]
- K Kanthiya, J Khunnarong, S Tangjitgamol, N Puripat, S Tanvanich. Expression of the p16 and ki67 in cervical squamous intraepithelial lesions and cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 2016. [Google Scholar]
- P L Cheah, C C Koh, A R Nazarina, K H Teoh, L M Looi. Correlation of p16INK4a immunoexpression and human papillomavirus (HPV) detected by in-situ hybridization in cervical squamous neoplasia. Malays J Pathol 2016. [Google Scholar]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Vedula B, V RRB, M R, R SRN, K SR. Expression of p16 in cervical premalignant and malignant lesions- IHC study [Internet]. Indian J Pathol Oncol. 2020 [cited 2025 Sep 10];7(3):404-407. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpo.2020.080
APA
Vedula, B., V, R. R. B., M, R., R, S. R. N., K, S. R. (2020). Expression of p16 in cervical premalignant and malignant lesions- IHC study. Indian J Pathol Oncol, 7(3), 404-407. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpo.2020.080
MLA
Vedula, Bharadwaj, V, Rama Reddy B, M, Rajani, R, Sree Ramulu Naidu, K, Srikanth Reddy. "Expression of p16 in cervical premalignant and malignant lesions- IHC study." Indian J Pathol Oncol, vol. 7, no. 3, 2020, pp. 404-407. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpo.2020.080
Chicago
Vedula, B., V, R. R. B., M, R., R, S. R. N., K, S. R.. "Expression of p16 in cervical premalignant and malignant lesions- IHC study." Indian J Pathol Oncol 7, no. 3 (2020): 404-407. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpo.2020.080
