Introduction
Upper GIT lesions involve esophagus, stomach and part of duodenum. Disorders of upper GIT are a frequent cause of clinical disease with inflammatory and neoplastic lesions being the most common.1 Esophagus and stomach are common sites of inflammatory processes which are easily treatable conditions whereas cancers of the esophagus and stomach are most lethal of all malignancies. Majority of these neoplasms are detected at an advanced stage due to similarity in benign causes of dysphagia and dyspepsia and due to insidious nature of the onset of symptoms.2 Esophageal cancer ranks sixth in mortality and stomach cancer fourth for mortality globally.3 The upper gastrointestinal flexible fiber optic endoscope was first used in 1968 and was a major breakthrough in the diagnosis of gastrointestinal tract (GIT) lesions. It provides a visual examination of the upper gastrointestinal tract using a flexible fiber optic or video endoscope which allows for easy inspection of GIT without any gaps. Endoscopic guided biopsy is an established diagnostic tool and is the current gold standard investigation for patients with upper GIT symptoms. It plays a crucial role in the management and surveillance of the conditions of upper GI tract and also in the follow up of patients.4
Objectives
To study the spectrum of neoplastic lesions of upper gastrointestinal tract and its correlation with socio-demographic details.
Materials and Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted for a period of one and a half years, from January 2019 to June 2020 at the Department of pathology, Mysore Medical College and Research Institute.
The present study included endoscopic biopsies of upper gastrointestinal tract. Biopsies that were reported as neoplastic lesions on endoscopy of Upper GIT were included in this study. A total of 50 cases were included in the study. Patients of all ages and both sexes with upper GI symptoms who underwent endoscopic biopsies were included in the study. Specimens were fixed, routinely processed and examined with H&E stain. Special stains like PAS and Giemsa stains was performed wherever necessary.
Clinical data was obtained from the case records, which included the age and sex of the patients, relevant habits if any, presenting symptoms, endoscopic findings and diagnosis.
The clinical and histological data so obtained were analyzed.
Results
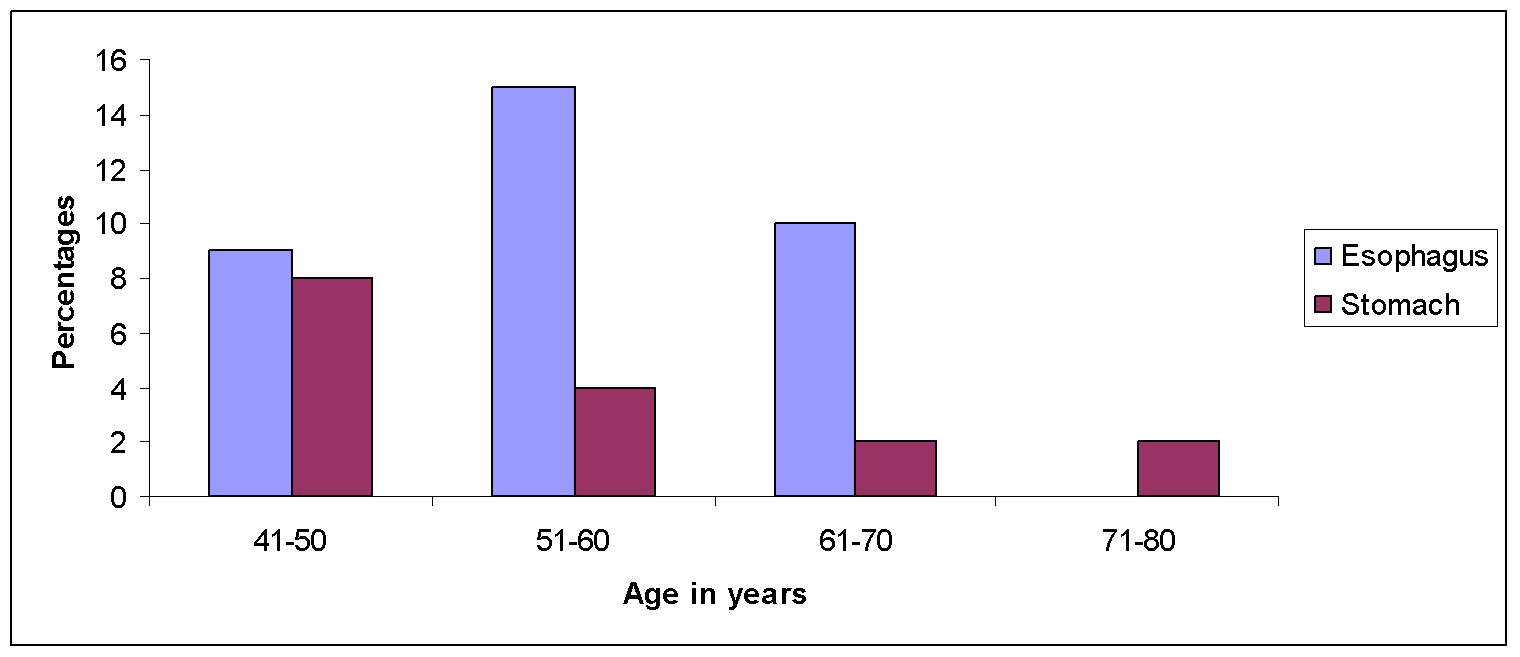
The study included 50 endoscopic biopsies from upper gastrointestinal tract reported as neoplastic lesions on endoscopy. The age of the patients varied from 41 to 80 years. The peak age incidence for gastric carcinomas was a decade earlier than esophageal cancers.
The study showed a slight male preponderance for all sites in the upper gastrointestinal tract with 35 (70%) male patients and 15 (30%) female patients. The male: female ratio was 2.3:1. (Figure 1)
The most common presenting complaint for patients with esophageal carcinoma was dysphagia and weight loss while patients with gastric carcinoma presented with dyspepsia or anorexia.
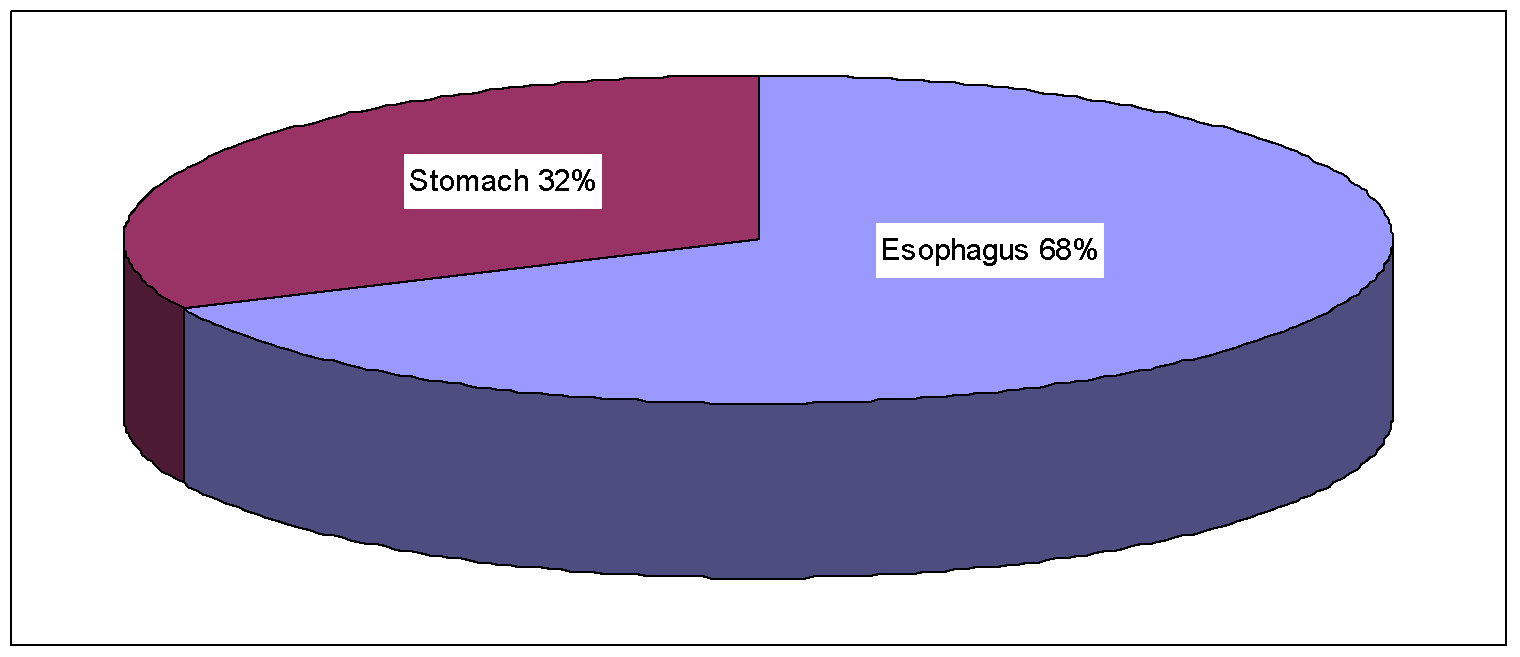
Site wise distribution of upper GI biopsies included 34 cases from esophagus (68%) and 16 cases from stomach (32%) Figure 2.
On histological assessment, all 50 endoscopic biopsies showed malignancy.
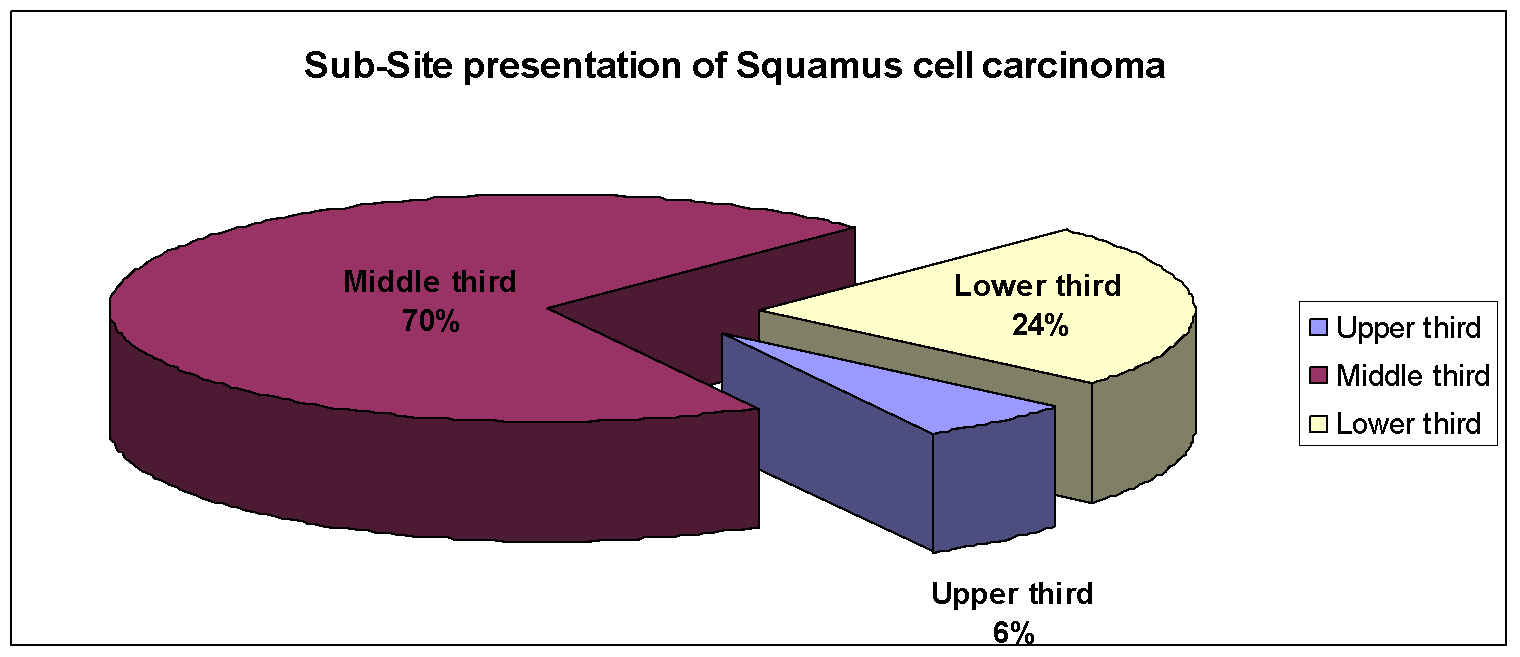
For esophageal malignancies the commonest site of presentation was the mid third of the esophagus (70.58%) followed by lower third (23.52%) and upper third (5.88%). (Figure 3)
The commonest esophageal malignancy encountered was squamous cell carcinoma (94%) with moderately differentiated SCC being the most commonly encountered SCC grade.
On endoscopy, the commonest type of presentation of SCC was polypoid growth (85%) followed by ulcerative (9%) and infiltrative (6%) lesions.
Out of 34 patients with esophageal neoplasms, 33 were betel nut chewers, 24 were smokers and 23 consumed alcohol. Similarly, out of 16 patients with gastric neoplasms 11 were smokers and 9 consumed alcohol. It was seen that habits like smoking and alcohol were seen exclusively in males while betel nut chewing was seen in almost equal proportions in males and females.
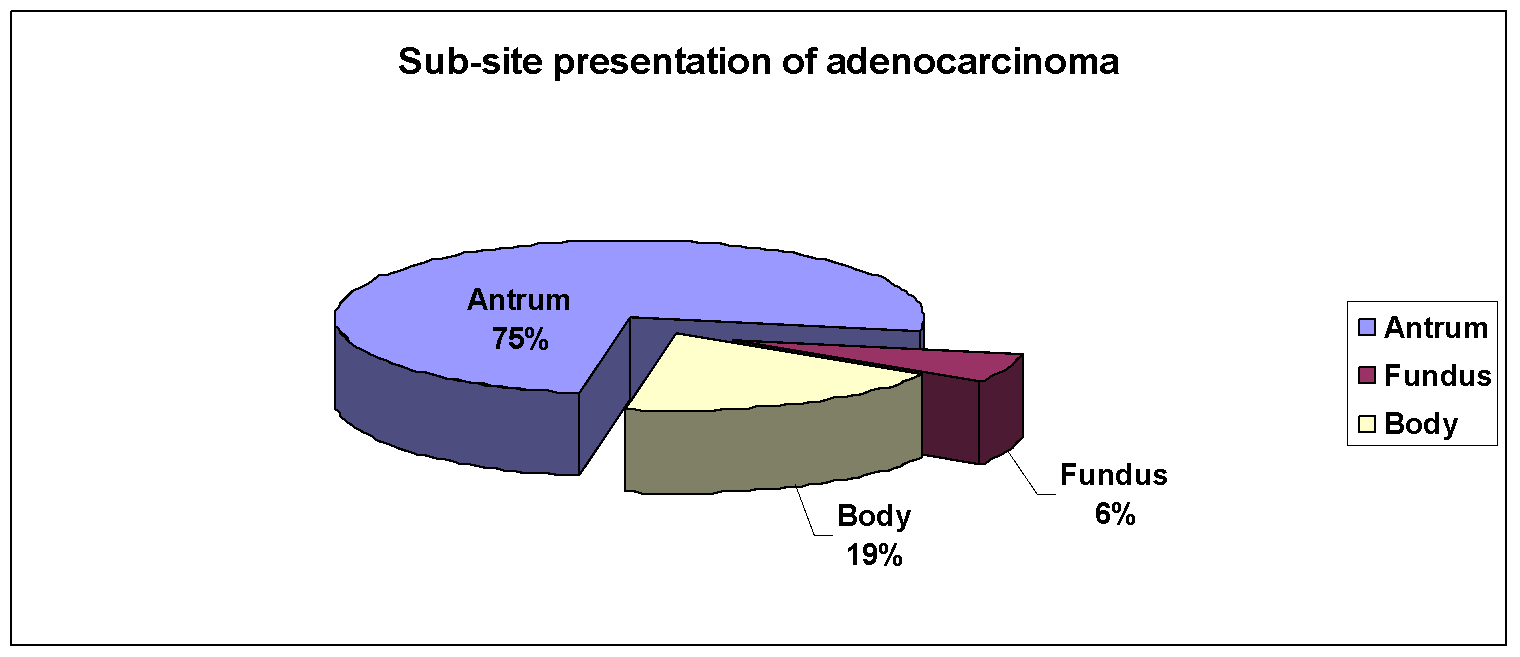
The commonest site of presentation of the gastric adenocarcinoma was the antrum, followed by the fundus and then the body (Figure 4). On endoscopy, the commonest pattern of presentation of the gastric adenocarcinomas was an ulcerative growth followed by infiltrative and polypoidal growths. (Table 1)
Table 1
Endoscopic presentation and histopathological diagnosis of gastric biopsies
|
Endoscopic presentation |
Adeno Ca |
Total No. (%) |
|
Ulcerative |
8 |
8 (50%) |
|
Infiltrative |
5 |
5 (31%) |
|
Polypoidal |
3 |
3 (19%) |
|
Total |
16 |
16 (100%) |
The present study included 16 cases of gastric adenocarcinoma. The most common histopathological type of the gastric adenocarcinoma was intestinal followed by diffuse including signet ring cell carcinomas. The intestinal adenocarcinomas were mostly moderately differentiated, with the remaining being well differentiated and poorly differentiated.
The various associated findings encountered in esophageal carcinomas were HPV related changes. In the present study of the 36 cases of SCC, viral changes were seen in 3 cases (8.33%).
The various associated findings encountered in gastric adenocarcinomas were H. pylori infection chronic atropic gastritis, intestinal metaplasia, and gastric polyps. Of the 16 cases of adenocarcinoma, 2 cases (12.5%) showed H. pylori infection. There were 1 case (6.25%) of chronic atrophic gastritis and 1 case of intestinal metaplasia. A single case of hyperplastic polyp associated with a moderately differentiated tubulo-capilary carcinoma presented as a polypoid growth in the antrum.
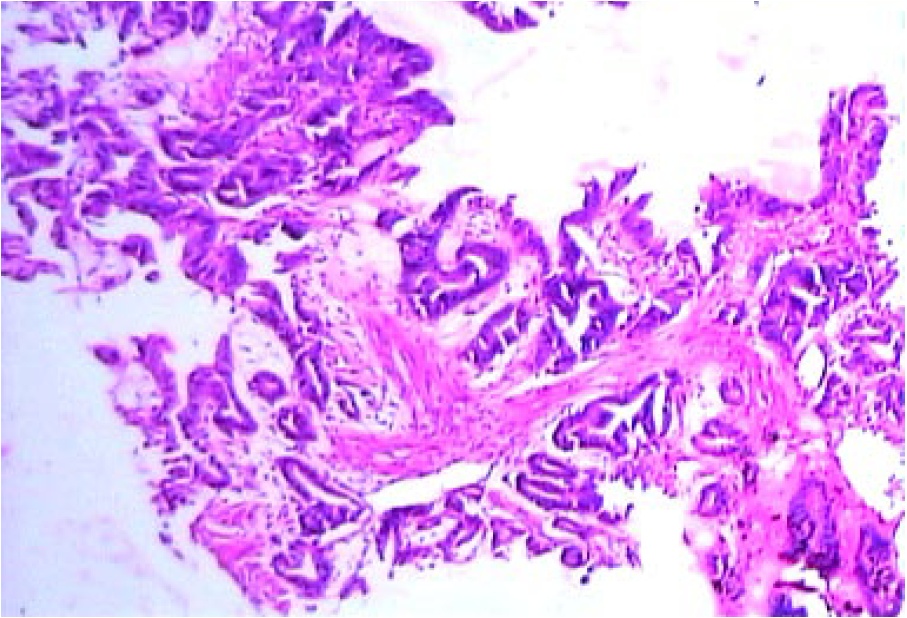
Figure 1
Well differentiated SCC-esophagus; showing epithelial pearls and koilocytosis of the overlying epithelium (H & E, 100x)
Discussion
Recent data suggests growing incidence of stomach cancers in young adults and increasing prevalence of esophageal cancers in East Asia.3 A total number of 87 endoscopic biopsies of upper gastrointestinal tract were received at the Pathology Department. Among which 50 were neoplastic lesions (57%) of upper gastrointestinal tract and were henceforth included in the present study. Similarly, in a study conducted by Vidyavathi K et al5 showed 58 neoplastic lesions out of 75 cases (77%).
In the present study most of the patients undergoing endoscopic biopsy were in the age group between 40 and 60 years. This was in concordance with studies done by Sunita Sharma et al4 and Saurabh Sharma et al.6
Patients undergoing endoscopic biopsies were predominantly males in the present study with male to female ratio of 2.3: 1 which was also observed in other studies done by Sandhya PG et al.,7 Rashmi K et al.8 and Shennak MM et al.9 The gender ratio favouring males could be because of fact that males are exposed to more risk factors like smoking, alcohol and other dietary factors than females.
In our study the most common site from which the biopsies were taken was esophagus followed by stomach which was in accordance with study conducted by Sunita Sharma et al4 whereas other studies like Jaynul Islam SM et al.10 and Sandhya PG et al.,7 showed stomach as the most commonly biopsied site. This could be because of the reason that esophageal cancer presents early and with specific signs and symptoms whereas gastric cancer presents with vague symptoms.11
In the present study, most common complaint for esophageal cancer was weight loss and dysphagia which is in accordance with the study by Amy Gallo et al11 whereas stomach cancer presented with symptoms like anorexia, weight loss and dyspepsia.
Esophageal biopsy
In our study, most common site of esophageal biopsy was middle-third, followed by lower-third and upper-third. Similar site distribution was also observed in studies done by Krishnappa Rashmi et al,12 Ganga H et al,13 Neha Satyanarayan Somani et al,14 Sunita Sharma et al.4
On histological examination, 32 cases (94%) of esophageal biopsies were reported as Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Among which, moderately differentiated carcinoma was the most frequently reported grade. 2 cases (6%) were reported as Adenocarcinoma of Esophagus. These findings are similar to the studies by Saurabh Sharma et al,6 Ganga H et al,13 Neha Satyanarayan Somani et al.14
Gastric biopsy
In our study, most common site for gastric biopsy was antrum followed by body and fundus.
On histological examination, 100% of stomach biopsies were reported as Adenocarcinoma. Similar findings were observed in studies conducted by Saurabh Sharma et al,6 Ganga H et al,13 Neha Satyanarayan Somani et al.14
On subtyping, 2 cases of diffuse adenocarcinoma (4%) comprising of signet ring cell carcinoma was seen which correlates with Vidyavathi et al5 and Qureshi NA15 study.
Conclusion
In the present study, the most commonly received endoscopic biopsy of upper gastrointestinal tract are esophageal followed by gastric biopsies. All the neoplasms encountered in the study were malignant. SCC was the commonest malignancy of the upper gastrointestinal tract and was seen solely in the esophagus. Patients with SCC of the esophagus had a strong habitual association with betel nut chewing, smoking and consumption of alcohol. Histologically, most of the SCCs were moderately differentiated carcinomas. The second common neoplasm in the upper GIT was adenocarcinoma which was seen in the stomach. The antrum was the commonest site for gastric adenocarcinomas. Histologically, intestinal and diffuse including signet ring cell carcinomas were seen.
The number of associated/predisposing lesions seen in upper GIT cancers were lesser as compared to other studies. This could be due to inadequate biopsy material from the surrounding sites.
To conclude, endoscopy of the gastrointestinal tract is diagnostic, though histopathology is the gold standard and aids in early detection of upper gastrointestinal lesions and better management.