- Visibility 170 Views
- Downloads 34 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijpo.2021.108
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Mixed mucinous carcinoma of breast – A case report
Introduction
Mucinous Carcinoma (MC) approximately accounts for 1-7% of breast carcinomas. It is most commonly seen in perimenopausal and postmenopausal women.[1], [2] Pure Mucinous Carcinoma (PMC) has a better prognosis as compared to ductal or lobular variants of breast cancer and Mixed Mucinous Carcinoma (MMC) has unfavourable prognosis with early nodal metastases.[3] Hence it is important to differentiate between the two variants of mucinous carcinoma.
Case History
We present a case of 70 year old female who came with the complaints of lump in the right breast since 2 months with no family history of breast cancer. On clinical examination, an irregular swelling of 2x1 cm was noted in upper outer quadrant and right axilla had a palpable swelling of 1x1cm. Ultrasound showed a well defined heterogenous lesion with few specks of calcification measuring 2.1x1.4cm at 10-12`o clock position involving the retroareolar region was seen and a BIRADS V score was given. Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) examination of breast was done and it was positive for malignant cells.
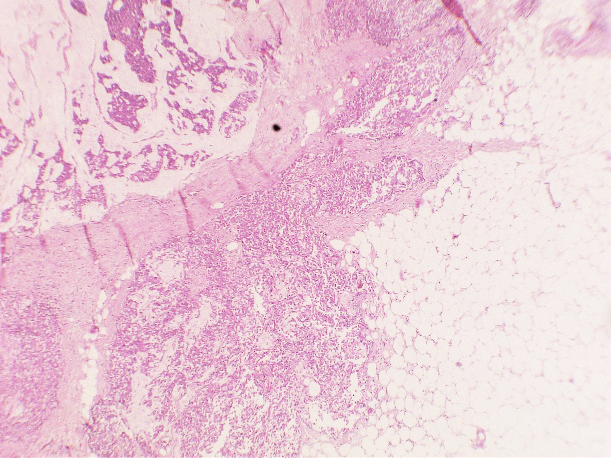
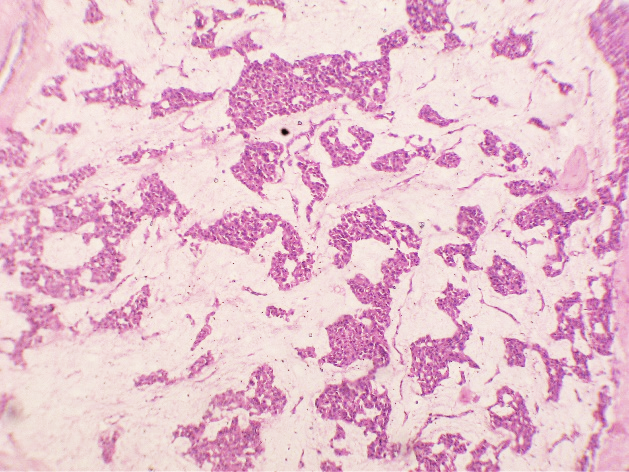
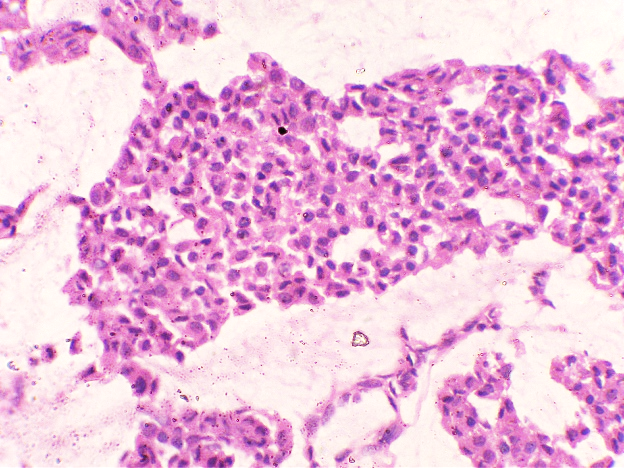
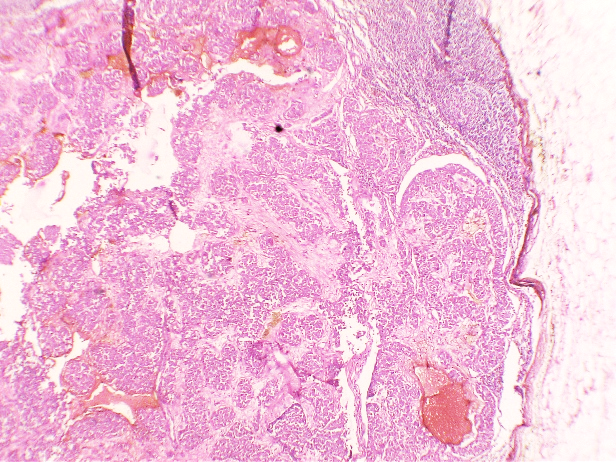
The patient underwent Right Modified mastectomy with right axillary dissection. On gross examination, a whitish hard tumour beneath Nipple Areolar Complex measuring 2x1cm with fibrous area and specks of calcification was noted. On Microscopic Examination, Sections from the tumour studied show a neoplasm composed of islands of tumour cells suspended in extracellular mucin (<30%) separated by thick fibrous septae – Capella Type B. Focal areas showing tumour cells arranged in solid nests. Individual tumour cells are oval with moderate eosinophilic cytoplasm and round to oval vesicular nuclei, mitosis is rare. Ductular formation is scanty. Multiple foci of intraductal carcinoma, solid type, cribriform type and comedo types seen. 3/13 lymph nodes were positive and margins were free of tumour.
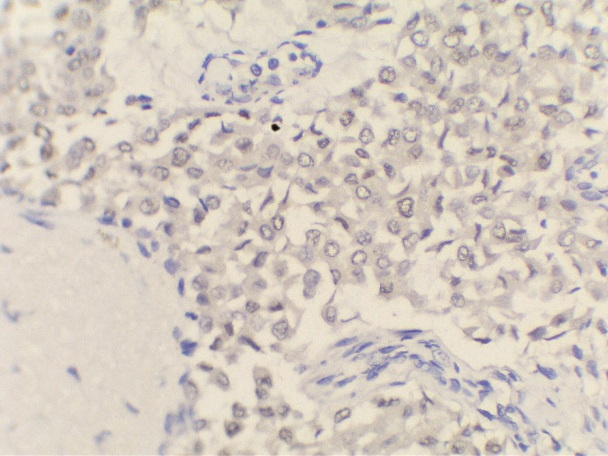
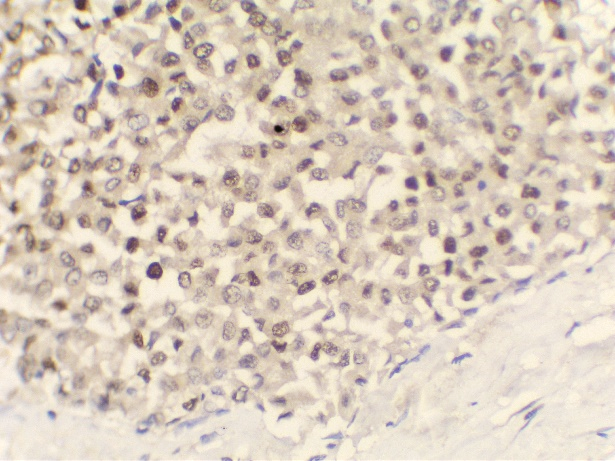
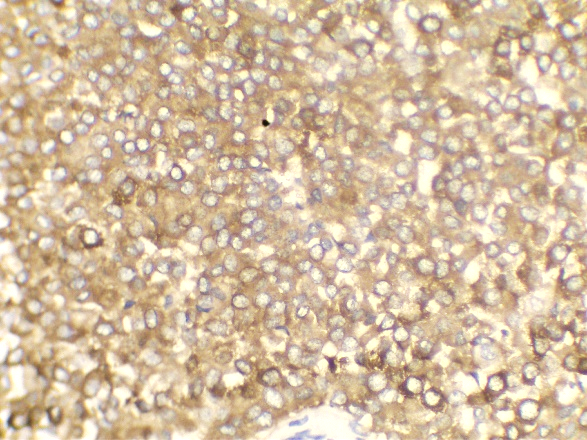
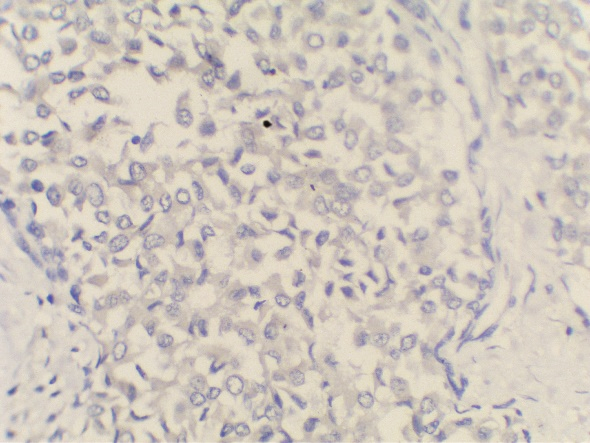
Immunohistochemistry was done –
ER, PR, Synaptophysin were positive and
Her2neu was negative.
Discussion
In our Institution, during last 3 years 50 cases of breast carcinoma were reported out of which only 3 cases i.e., 6% were mucinous adenocarcinoma of breast. FNAC was done in this case which was positive for malignancy.
MC is a relatively rare histological subtype that is characterized by neoplastic cells that are arranged in sheets or clusters and are suspended in extracellular mucin. In PMC, mucinous component is >90% consisting of solely of tumor tissue with extracellular mucin production.[1] MMC has 10-90% of mucin along with invasive ductal epithelial component. Based on the cellularity and endocrine differentiation, two types of MC has been suggested. Capella type A shows scattered small epithelial clusters, strips or cribriform structures floating in pools of extracellular mucin. Capella type B shows large sheets of tumor cells with mucin production and neuroendocrine features which was confirmed by Synaptophysin IHC in this case.[4], [5] Most of the MC cases are ER, PR Positive and Her2neu negative. MMC have higher rate of nodal involvement.[6]
It is important to differentiate MC from non-neoplastic mucocele like lesions.[7] The absence of cytological atypia in epithelial lining of mucin filled ducts and presence of myoepithelial cells in pools of mucin which are extravasated in stroma due to rupture of cystically dilated mucin filled are features of mucocele like lesions.
Conclusion
In view of nodal involvement, it is important to differentiate between PMC and MMC. PMC usually shows a better prognosis and a lower lymph node metastatic rate compared to MMC.[8] Adjuvant endocrine therapy is indicated for hormone responsive tumors as most of mucinous carcinomas are positive for estrogen receptor and/or progesterone-receptor. [9], [7]
Abbreviations
IHC – Immunohistochemistry; MC - Mucinous carcinoma; PMC - Pure Mucinous Carcinoma; MMC - Mixed Mucinous Carcinoma; FNAC - Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology; BIRADS - Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System; ER – Estrogen Receptor; PR – Progesterone Receptor
Source of Funding
None.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- P Sun, Z Zhong, Q Lu, M Li, X Chao, D Chen. Mucinous carcinoma with micropapillary features is morphologically, clinically and genetically distinct from pure mucinous carcinoma of breast. Modern Pathol 2020. [Google Scholar]
- HA Haddad, Awadia Awadallah, MA Hadi. Mucinous breast carcinoma: Report of four cases and review of the literature. Clin Diagn Pathol 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- CI Li. Risk of mortality by histologic type of breast cancer in the United States. Horm Cancer 2010. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- S Park, J Koo, JH Kim, WI Yang, BW Park, KS Lee. Clinicopathological characteristics of mucinous carcinoma of the breast in Korea: comparison with invasive ductal carcinoma-not otherwise specified. J Korean Med Sci 2010. [Google Scholar]
- B Weigelt, FC Geyer, HM Horlings, B Kreike, H Halfwerk, JS Reis-Filho. Mucinous and neuroendocrine breast carcinomas are transcriptionally distinct from invasive ductal carcinomas of no special type. Modern Pathology 2009. [Google Scholar]
- JC Paramo, C Wilson, D Velarde, J Giraldo, RJ Poppiti, TW Mesko. Pure mucinous carcinoma of the breast: is axillary staging necessary?. Ann Surg Oncol 2002. [Google Scholar]
- T Nakagawa, K Sato, M Moriwaki, R Wada, A Arakawa, M Saito. Successful endocrine therapy for locally advanced mucinous carcinoma of the breast. Breast J 2012. [Google Scholar]
- P Skotnicki, B Sas-Korczynska, L Strzepek, J Jakubowicz, P Blecharz, M Reinfuss. Pure and mixed mucinous carcinoma of the breast: a comparison of clinical outcomes and treatment results. Breast J 2016. [Google Scholar]
- A Ranade, R Batra, G Sandhu, R A Chitale, J Balderacchi. Clinicopathological evaluation of 100 cases of mucinous carcinoma of breast with emphasis on axillary staging and special reference to a micropapillary pattern. Journal of clinical pathology 2010. [Google Scholar]
How to Cite This Article
Vancouver
Gupta M, S ML, Josephine A, Gali V. Mixed mucinous carcinoma of breast – A case report [Internet]. Indian J Pathol Oncol. 2021 [cited 2025 Sep 13];8(4):518-521. Available from: https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpo.2021.108
APA
Gupta, M., S, M. L., Josephine, A., Gali, V. (2021). Mixed mucinous carcinoma of breast – A case report. Indian J Pathol Oncol, 8(4), 518-521. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpo.2021.108
MLA
Gupta, Mohini, S, Mary Lilly, Josephine, A, Gali, Vinutha. "Mixed mucinous carcinoma of breast – A case report." Indian J Pathol Oncol, vol. 8, no. 4, 2021, pp. 518-521. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpo.2021.108
Chicago
Gupta, M., S, M. L., Josephine, A., Gali, V.. "Mixed mucinous carcinoma of breast – A case report." Indian J Pathol Oncol 8, no. 4 (2021): 518-521. https://doi.org/10.18231/j.ijpo.2021.108
